CBD BIOACTIVITY AND VALVULAR INTERSTITIAL CELL CALCIFICATION
ABSTRACT
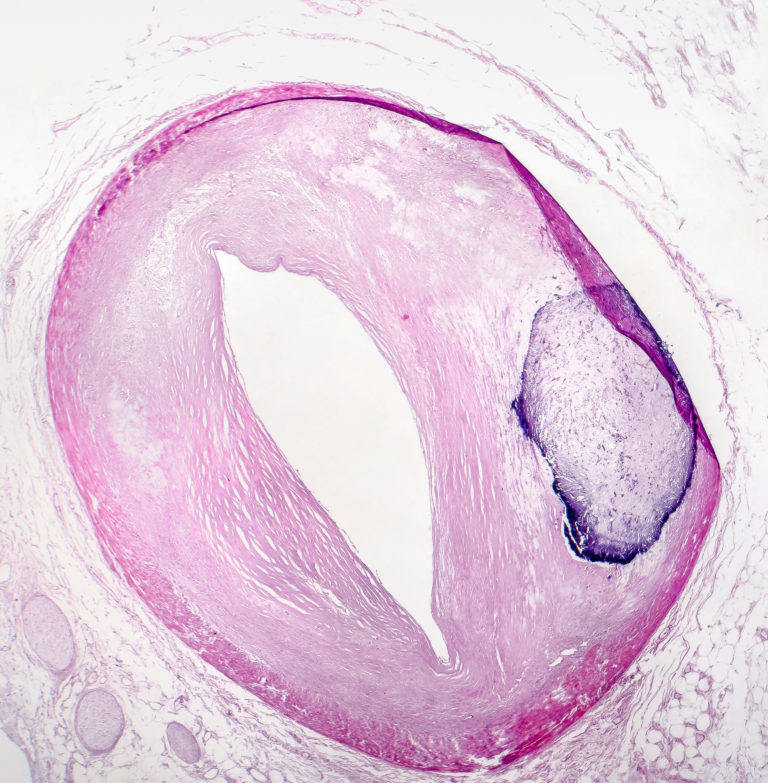
Valvular interstitial cells (VICs) are integral to heart valve homeostasis and structural leaflet integrity. Aberrant calcification of VICs leads to dangerous diseases including calcific aortic valve disease. VIC calcification can be reduced by cannabidiol (CBD) through modulation of the ERK cascade by selective antagonism of the CB2 receptor, and possible involvement of the GPR55 receptor. ß-Caryophyllene (BCP) and α-Humulene (HMU) are sequiterpenes that produce their own effects on calcification. The present study aimed to see whether a combination of CBD, BCP, and HMU (ImmunAG) could reduce calcification to a greater extent than CBD alone. VICs were isolated from porcine aortic valve leaflets, induced to calcify, and treated with CBD or ImmunAG. Treatment concentrations of 5, 10, 25, 40, and 100 mg were examined. Means, standard deviations, minimum, and maximum calcification reduction values for each treatment and mg concentration are provided. 5 t-tests revealed that ImmunAG reduced calcification more than CBD at every concentration.